Radiators for heat pump.
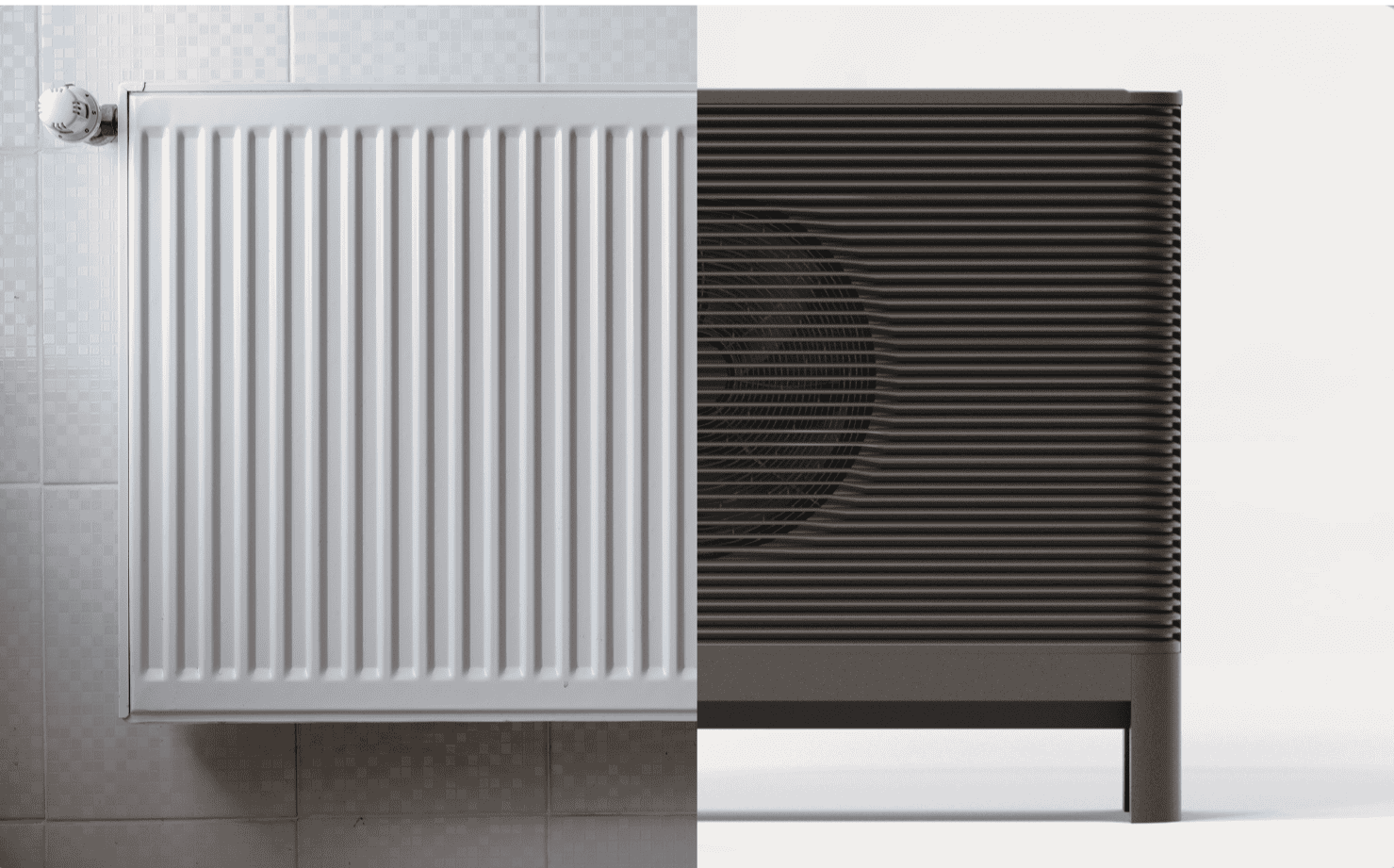

To fully utilize the performance of a heat pump, it is important to choose appropriately radiators that work with the low water temperatures produced by heat pumps. While traditional burners and boilers require water at high temperatures (above 60°C), heat pumps operate more efficiently with water at lower temperatures (around 35-45°C). Consequently, the radiators that will be used must be able to transfer heat effectively at these lower temperatures.
Types of Radiators for Heat Pumps
- Larger Radiators (Larger Surface Bodies)
- The larger radiators They are more efficient when they use water at a lower temperature. The larger surface area of the radiator allows for better efficiency in transferring heat to the air in the room. These units require less heat to provide the same amount of heat compared to more traditional radiators.
- Underfloor Heating
- THE underfloor heating is one of the best solutions for heat pump systems, as it operates with very low water temperatures (30-40°C). The larger floor surface allows for more uniform and efficient heat dissipation, and heat pumps operate very efficiently with such systems.
- Aluminum or Steel Bodies (More Efficient)
- The aluminum the copper radiators They are more efficient at transferring heat, as they have better thermal conductivity. These radiators will cope better with low water temperatures than traditional cast iron radiators.
- Electric Heating Elements (Surface Elements)
- There are also electric heating elements that are compatible with heat pumps, especially in spaces that require a smaller amount of heat or where underfloor heating is not feasible.
Characteristics of Radiators for Heat Pumps
- Low Operating Temperature
As mentioned, heat pumps are most efficient when the water circulating in the radiators is at a low temperature (35-45°C). Therefore, the radiators must be able to heat the space with a low water temperature. This means that they must have larger surface area or operate in lower temperatures to deliver the right amount of heat. - Efficiency and Design
The design of radiators plays a role in efficiency. More modern designs (e.g. smoother and more aerodynamic radiators, aluminum or copper surfaces) are more efficient at transferring heat from the water to the room air, without requiring high water temperatures. - Larger Surface for Heat Distribution
Radiators that have a larger surface area, such as long narrow radiators or the underfloor heating systems, can operate efficiently with lower water temperatures. This allows for better heat dissipation in the space without the need for high temperatures.
Advantages of Using Radiators with Heat Pumps
- Greater Energy Efficiency
By using the appropriate radiators, the heat pump can deliver maximum energy efficiency, reducing operating costs and increasing the lifespan of the system. - Uniform Heating
Better heat dissipation from the right radiators offers more uniform heating throughout the space. - Space Saving
By choosing underfloor heating, for example, you save wall space and can improve the aesthetics of the space, without requiring the installation of bulky radiators.
Conclusions
For the heat pump heating system to operate efficiently, it is crucial to select suitable radiators that can take advantage of the low water temperatures provided by the heat pump. The best options include larger radiators, underfloor heating and efficient aluminum or steel bodiesThis ensures high energy efficiency and reduced operating costs for the heat pump installation.


 Piping - Insulation
Piping - Insulation  Piping Fittings
Piping Fittings  Valves - Cannulas
Valves - Cannulas  Drains
Drains  Water tanks - Accessories
Water tanks - Accessories  Support - Tables
Support - Tables  Spiral
Spiral  24x19 components
24x19 components  Welding - Sealing
Welding - Sealing  Water filter
Water filter  Various Plumbing Items
Various Plumbing Items 
 Water tanks
Water tanks  Bathroom Sinks
Bathroom Sinks  Tiles
Tiles  Bathroom accessories
Bathroom accessories  Mirrors
Mirrors  Ventilation Accessories
Ventilation Accessories  Bathroom lighting
Bathroom lighting  Basin Covers
Basin Covers  Basins
Basins  Shower Columns
Shower Columns  Bathroom furnishings
Bathroom furnishings  Bathroom cabins
Bathroom cabins  Showers
Showers  Sinks
Sinks 
 Kitchen faucets
Kitchen faucets  Bathroom batteries
Bathroom batteries  Sink batteries
Sink batteries  Built-in batteries
Built-in batteries  Bidet faucets
Bidet faucets  Battery Spare Parts
Battery Spare Parts 
 Fireplaces
Fireplaces  Boilers - Burners
Boilers - Burners  Heat pumps
Heat pumps  Circulators
Circulators  Heating Devices
Heating Devices  Radiator bodies
Radiator bodies  LPG accessories
LPG accessories  accessory
accessory  Spare parts
Spare parts  Heating accessories
Heating accessories  Chimneys
Chimneys  Plastic tanks
Plastic tanks  Air conditioners
Air conditioners  Fans
Fans  Dehumidifiers
Dehumidifiers 
 Sockets - Switches
Sockets - Switches  Paintings
Paintings  Electrical Boxes - Buat
Electrical Boxes - Buat  Raga materials
Raga materials  Lightning Protection & Grounding
Lightning Protection & Grounding  Fishing Reels - Extensions
Fishing Reels - Extensions  Plug - Socket - Power socket - Adapters
Plug - Socket - Power socket - Adapters  Intercoms - Intercoms
Intercoms - Intercoms  Dui
Dui  Channels - Accessories
Channels - Accessories  UPS - Voltage Stabilizers
UPS - Voltage Stabilizers  Absorbers
Absorbers  Television Accessories - Antennas
Television Accessories - Antennas  Connection & Support Materials
Connection & Support Materials  Various Industrial Facilities
Various Industrial Facilities  Installation Pipes
Installation Pipes  Various materials
Various materials  Alarms & Accessories
Alarms & Accessories  Cables
Cables  Consumables
Consumables 
 LED lamps
LED lamps  Headlights
Headlights  Indoor Lighting
Indoor Lighting  Outdoor Lighting
Outdoor Lighting  LED Power Supplies - Controllers & Dimmers
LED Power Supplies - Controllers & Dimmers  LED strips
LED strips  Decorative
Decorative  Various Lamps
Various Lamps  Fluorine lamps
Fluorine lamps  Professional Lighting
Professional Lighting  Halogen lamps
Halogen lamps  Linear Luminaires
Linear Luminaires  Rails - LED Rail Lights
Rails - LED Rail Lights  accessory
accessory  Pear
Pear  G9 & G4
G9 & G4  Tube
Tube  Special Applications
Special Applications  Candle
Candle  Spot - GU10 - Studs
Spot - GU10 - Studs  Globe
Globe  Mirror
Mirror 
 Boiler
Boiler  Solar
Solar  Inertia Containers
Inertia Containers  Solar cover
Solar cover  Water heaters
Water heaters  Wood-Electric Water Heaters
Wood-Electric Water Heaters 
 Hand tools
Hand tools  Blades & Blades
Blades & Blades  Cleaners - Technical Sprays
Cleaners - Technical Sprays  Toolboxes
Toolboxes  Protective Items
Protective Items  Water pumps
Water pumps  Cutting Discs
Cutting Discs  Drills - Bits
Drills - Bits  Building materials
Building materials  Adhesive Films
Adhesive Films  Cleaning Brushes
Cleaning Brushes  Connections-Watering Fittings
Connections-Watering Fittings  Water Guns/Throwers
Water Guns/Throwers  Compressors - Vacuums
Compressors - Vacuums  Various materials
Various materials 

 Piping - Insulation
Piping - Insulation Piping Fittings
Piping Fittings Valves – Cannulas
Valves – Cannulas Drains
Drains Tanks - Accessories
Tanks - Accessories Support – Tables
Support – Tables Spiral
Spiral 24×19 fittings
24×19 fittings Welding - Sealing
Welding - Sealing Water filter
Water filter Various Plumbing Items
Various Plumbing Items Water tanks
Water tanks Bathroom Sinks
Bathroom Sinks Tiles
Tiles Bathroom accessories
Bathroom accessories Mirrors
Mirrors Bathroom lighting
Bathroom lighting Ventilation Accessories
Ventilation Accessories Basin Covers
Basin Covers Basins
Basins Shower Columns
Shower Columns Bathroom cabins
Bathroom cabins Showers
Showers Sinks
Sinks Bathroom batteries
Bathroom batteries Sink batteries
Sink batteries Built-in batteries
Built-in batteries Bidet faucets
Bidet faucets Battery Spare Parts
Battery Spare Parts Fireplaces
Fireplaces Boilers - Burners
Boilers - Burners Heat pumps
Heat pumps Circulators
Circulators Heating Devices
Heating Devices Radiator bodies
Radiator bodies LPG accessories
LPG accessories accessory
accessory Spare parts
Spare parts Heating accessories
Heating accessories Chimneys
Chimneys Plastic tanks
Plastic tanks Air conditioners
Air conditioners Fans
Fans Dehumidifiers
Dehumidifiers Sockets - Switches
Sockets - Switches Paintings
Paintings Electrical Boxes - Buat
Electrical Boxes - Buat Raga materials
Raga materials Lightning Protection & Grounding
Lightning Protection & Grounding Fishing Reels – Extensions
Fishing Reels – Extensions Plug - Socket - Power socket - Adapters
Plug - Socket - Power socket - Adapters Dui
Dui Channels – Accessories
Channels – Accessories UPS – Voltage Stabilizers
UPS – Voltage Stabilizers Television Accessories – Antennas
Television Accessories – Antennas Connection & Support Materials
Connection & Support Materials Various Industrial Facilities
Various Industrial Facilities Installation Pipes
Installation Pipes Various materials
Various materials Alarms & Accessories
Alarms & Accessories Cables
Cables Consumables
Consumables Water heaters
Water heaters Solar
Solar Boiler
Boiler Wood-Electric Water Heaters
Wood-Electric Water Heaters LED lamps
LED lamps Headlights
Headlights Indoor Lighting
Indoor Lighting Outdoor Lighting
Outdoor Lighting LED Power Supplies – Controllers & Dimmers
LED Power Supplies – Controllers & Dimmers LED strips
LED strips Decorative
Decorative Various Lamps
Various Lamps Fluorine lamps
Fluorine lamps Professional Lighting
Professional Lighting Halogen lamps
Halogen lamps Linear Luminaires
Linear Luminaires Tracks – LED Track Lights
Tracks – LED Track Lights accessory
accessory Hand tools
Hand tools Blades & Blades
Blades & Blades Cleaners - Technical Sprays
Cleaners - Technical Sprays Toolboxes
Toolboxes Protective Items
Protective Items Water pumps
Water pumps Cutting Discs
Cutting Discs Drills – Bits
Drills – Bits Building materials
Building materials Adhesive Films
Adhesive Films Cleaning Brushes
Cleaning Brushes Connections-Watering Fittings
Connections-Watering Fittings Compressors – Vacuums
Compressors – Vacuums Water Guns/Throwers
Water Guns/Throwers Various materials
Various materials